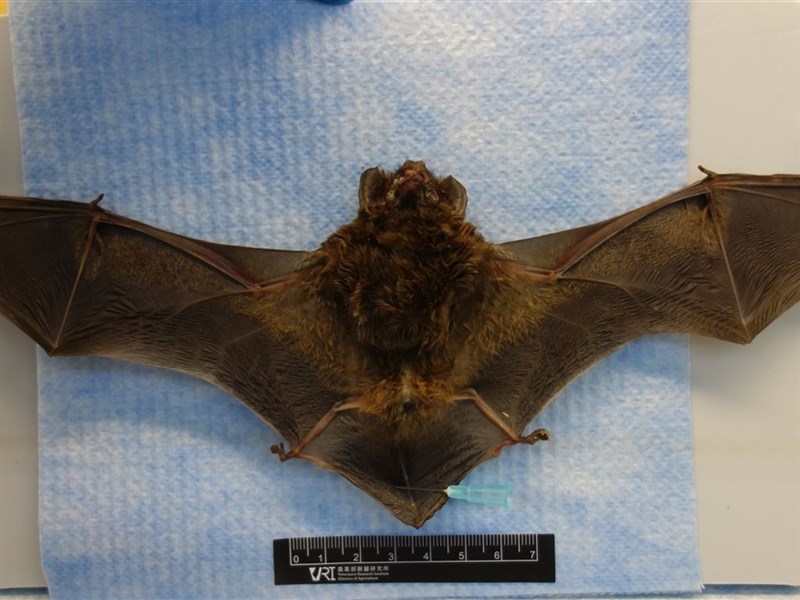
2024/4/25 16:19 (updated at 4/25 16:50)
Recently, people in Zhonghe District, New Taipei City picked up a Jungshan bat, and Taiwanese bat lyssavirus type 2 was detected. Although it is not a statutory animal infectious disease and there are currently no cases of human infection, it is a common risk for humans and animals. (Provided by the National Defense Inspectorate)
(Central News Agency reporter Zeng Yining, Taipei, 25th) Recently, people in Zhonghe District, New Taipei City picked up Rongshan bats, and Taiwanese bat lyssavirus type 2 was detected. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reminded today that there are currently no cases of human infection with this virus, but there is still a risk of zoonotic transmission, and it is reminded not to come into contact with wild animals.
The Animal and Plant Inspection and Quarantine Service of the Ministry of Agriculture announced that on the 22nd, the Veterinary Research Institute of the Ministry of Agriculture received assistance from the Taipei Bat Conservation Association and sent for inspection a Nyctalus plancyi velutinus found at home by people in Zhonghe District. It was detected in Taiwan. bat lyssavirus
Lyssa virus encyclopedia
The genus Lyssavirus is a branch of the Rhabdoviridae family. Currently, there are 16 species of lyssavirus in the genus Lyssavirus recognized by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. There are also 2 species of viruses (the Animal Health Institute detected them in Taiwanese domestic bats in East Asia). Bat lyssavirus and Kotalahti bat lyssavirus detected in bats in Finland) are yet to be approved.
- The most well-known genus Lyssavirus is Rabies lyssavirus, which is distributed almost all over the world and has a wide range of hosts. Other lyssaviruses are more geographically restricted and restricted to specific host species.
- Rabies virus can cause acute viral encephalomyelitis. In addition to cases of rabies virus infecting humans, six other lyssaviruses also infect humans.
- Treatment: If you are accidentally scratched and bitten by a wild animal, please wash the wound with soap and plenty of water for 15 minutes, disinfect with betadine or 70% alcohol, and go to the “Human Rabies Vaccination Service Hospital (Health Clinic)” as soon as possible for medical treatment .
- Prevention: Do not touch or catch wild animals. Pets at home must be vaccinated against rabies every year.
Source: Ministry of Agriculture, CDC
See more
closure
Type II.
Regarding the people who found the bat this time, CDC spokesperson Zeng Shuhui said in an interview with the media today that after contacting the public, the case was discovered at home and the bat was not moving and was sent to the relevant unit. She was not bitten by the bat and was not exposed in the assessment. risk, so post-exposure vaccination is not required for the time being.
According to the CDC, rabies virus can cause acute viral encephalomyelitis, with a fatality rate of nearly 100%. Tsang Shu-hui said that Taiwanese bat lyssavirus type 2 and rabies virus (RABV) are classified in the same genus but are different viruses. Although there are currently no human infection cases of this virus in Taiwan, there have been cases of human infection with lyssavirus in other countries. As for the fatal cases, it is estimated that there is still a risk of zoonosis, and there is concern that the fatality rate and severity of the disease may be similar to rabies, so the public is reminded to pay attention.
If the public finds weak or dead bats, Zeng Shuhui said it is recommended to notify the local bat conservation group or animal epidemic prevention agency for handling; and calls on the public not to contact or capture wild animals, and to take their pets at home to receive rabies vaccinations every year; if they are accidentally encountered by wild animals, If you are scratched or bitten by an animal, please wash the wound with soap and plenty of water for 15 minutes, then disinfect with betadine or 70% alcohol, and then go to the “Human Rabies Vaccination Service Hospital (Health Clinic)” for medical treatment as soon as possible.
According to monitoring data from the Ministry of Agriculture, a total of 6 cases of lyssavirus have been detected in bats in China since 2016, including 1 case each in Tainan City, Yunlin County, Keelung City, Yilan County, and 2 cases in New Taipei City.
According to the CDC, international literature research reports indicate that for post-exposure vaccination against suspected Lyssavirus, rabies immune globulin can be used to infiltrate wounds to neutralize the virus. Rabies vaccination can also be used against Taiwanese bat Lyssavirus type 2. With cross-protective effect.
The CDC pointed out that people who are exposed to ferret badgers, white-nosed rats, rat rats (limited to Taitung City), bats, and “animals that exhibit obvious special and abnormal behavior and are suspected of being infected with rabies virus or lyssa virus by the central agricultural administration unit” Animal scratches and bites will be assessed by professional physicians based on the wound exposure level classification, exposure location, county and city where the animal epidemic occurred, and other information. Rabies immune globulin and rabies vaccine will be injected, and 4 doses of post-exposure vaccine will be administered on time. (Editor: Chen Zhengwei) 1130425
Central News Agency “First-hand News” app
The text, pictures and videos on this website may not be reproduced, publicly broadcast or publicly transmitted and used without authorization.