Prevalence of Genital HPV Infection in Men:
A new study published in The Lancet Global Health reveals that approximately 1 in 3 males aged 15 and over are infected with at least one type of genital human papillomavirus (HPV). Moreover, 1 in 5 males are infected with one or more high-risk or oncogenic types of HPV. The study, conducted by Laia Bruni’s research team at the Catalan Institute of Oncology in Spain, analyzed the prevalence of genital HPV infection in men based on studies published between 1995 and 2022.
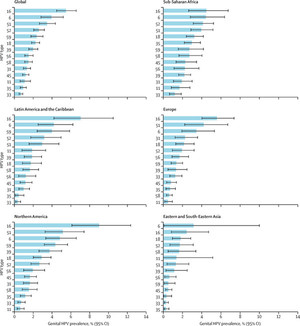
The study found that the global prevalence of HPV infection was 31%, while the prevalence of high-risk HPV infection was 21%. Among the HPV genotypes, HPV-16 was found to be the most common (5%), followed by HPV-6 (4%). Interestingly, the number of HPV cases peaked between the ages of 25 and 29 and remained high in young adults, stabilizing or slightly decreasing thereafter.
When analyzing the prevalence estimates by geographic regions, the study revealed similar rates for Europe, North America, Sub-Saharan Africa, Latin America, the Caribbean, Australia, and New Zealand (Oceania) – all falling in the range of the global prevalence. However, the estimates for East Asia and South East Asia were approximately half of those observed in other regions.
Impact and Consequences of HPV Infection:
While most cases of HPV infection in both men and women are asymptomatic, the long-term consequences can be severe, even leading to death. Cervical cancer alone claims the lives of over 340,000 women annually, emphasizing the urgent need for prevention and control measures.
In men, HPV infection typically manifests as anogenous warts, causing significant morbidity. It also increases the risk of HPV infection transmission. Moreover, HPV infection is associated with various cancers, including penile, rectal, and oropharyngeal cancers, with HPV 16 being frequently implicated.
The Hidden Source of Genital HPV Infection:
This study sheds light on a crucial finding – men are often the hidden source of genital HPV infection. Recognizing this, it becomes imperative to involve men in efforts to control HPV infection and reduce the incidence of HPV-related diseases in both sexes. Researchers assert that ongoing efforts should focus on preventing HPV infection and reducing the burden of HPV-related diseases in men and women alike.
About 1 in 3 males aged 15 and over are infected with at least one type of genital human papillomavirus (HPV), and 1 in 5 are infected with one or more high-risk or oncogenic types of HPV, according to a new study in the September issue of The Lancet Global Health was published on
Laia Bruni’s research team at the Catalan Institute of Oncology in Spain systematically analyzed the prevalence of genital HPV infection in the general male population based on studies published between 1995 and 2022.
The study found that the combined global prevalence was 31% for HPV and 21% for high-risk HPV.
HPV-16 was the most common HPV genotype (5%), followed by HPV-6 (4%).
The number of HPV cases peaked between the ages of 25 and 29, was high in young adults, and then stabilized or decreased slightly.
Pooled prevalence estimates were similar for the United Nations Sustainable Development Goal geographic regions of Europe, North America, Sub-Saharan Africa, Latin America, the Caribbean, Australia and New Zealand (Oceania).
The estimates for East Asia and South East Asia were half of the estimates for the other regions.
Most cases of HPV infection in men and women are asymptomatic, but can lead to long-term sequelae and death.
More than 340,000 women die from cervical cancer every year.
In men, HPV infection tends to manifest clinically as anogenous warts, which cause significant morbidity and increase the rate of HPV infection.
HPV infection is also associated with penile, rectal and oropharyngeal cancers, which are commonly associated with HPV 16.
“This finding demonstrates that men are often the hidden source of genital HPV infection and the importance of involving men in efforts to control HPV infection and reduce the incidence of HPV-related disease in both sexes,” the researchers wrote. .
“We must continue to look for opportunities to prevent HPV infection and reduce the incidence of HPV-related diseases in men and women,” he added.
Combined prevalence of HR-HPV, HPV-6, and HPV-11 types in men by region
Send article to SNS Send article to Facebook Send article to Twitter Send article to Kakao Story Copy URL Send article to Email Send article Find another share Scrap article
#men #worldwide #infected #HPV