industry
Entered 2024.04.29 18:21 Modified 2024.04.30 01:38 Paper A5
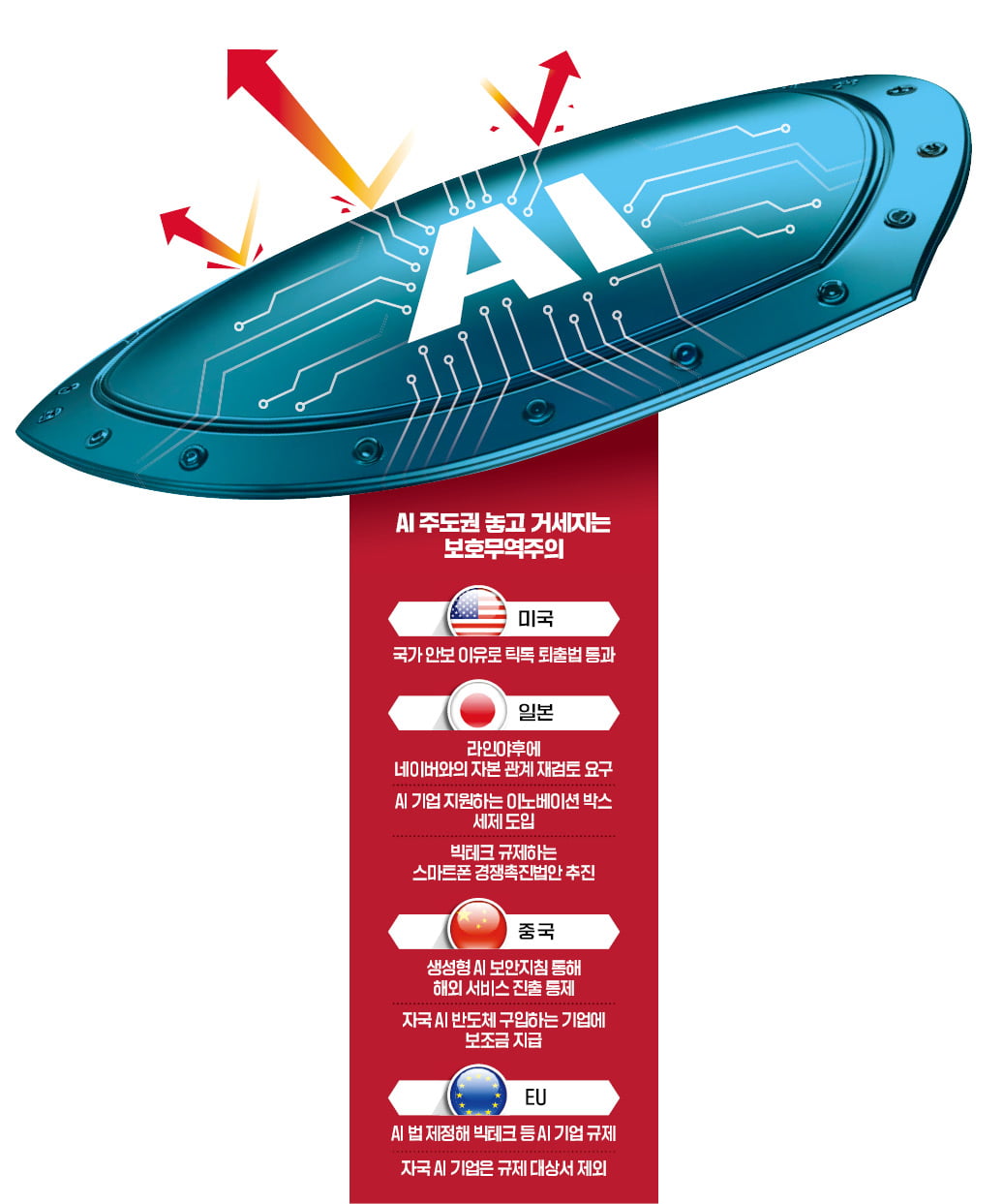
A global ‘tsunami of AI protectionism’
“If the hegemony of AI is removed, it’s over”… Related companies are also subject to heavy fines when they monopolizeJapan is introducing a smartphone competition law this month
Prevent showing your own apps with priority during searches
Limit interference with competitors’ app markets
In the event of a breach, a fine of up to 20% of sales is imposed.The EU is seriously regulating ‘Big Tech AI’
If you break the law, you will be fined 7% of global sales.
With the exception of European companies such as France and GermanyKorea is taking steps to repeal the ‘AI law’ in the National Assembly
To dominate artificial intelligence (AI) technology, governments around the world are raising protectionist barriers. They do not hesitate to provide subsidies and tax benefits to domestic companies, but they do not hesitate to put foreign companies at an open disadvantage. The common view of governments in all countries is that if leadership is taken away during the market formation period, it will be difficult to catch up.
Japan provides subsidies and tax benefits
According to the information technology (IT) industry on the 29th, the Japanese government plans to introduce a smartphone competition promotion bill to the National Assembly this month to regulate the monopolistic behavior of big technology. This bill prohibits companies from displaying their services in front of other companies in search results and also restricts actions that interfere with other companies’ provision of app markets. If the law is broken, a fine of up to 20% of sales in Japan can be imposed. The industry assessment is that it is aimed at major global technology companies such as Google and Apple.
In the same context last month, the Japanese government asked Line Yahoo, which serves Japan’s national messenger line, to review its capital relationship with Naver. The Japanese government believes that Line Yahoo did not properly manage user information due to its reliance on Naver, the main shareholder and trustee of the system and network business, and that user information was leaked because of this. The dominant opinion in Japan is that they are wary of Naver, which is expanding into various fields such as messengers, AI, content, and commerce.
There are no companies in Japan that are getting global attention in the field of AI. For this reason, the Japanese government seems to actively support companies. The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry provided subsidies worth 5.3 billion yen (about 46.5 billion won) for the purchase of supercomputers necessary for Softbank’s productive AI development. The Innovation Box Tax System was recently established to support companies in the AI software and service fields. You can receive a tax deduction of up to 30% on license income and transfer income arising from patents and intellectual property rights related to AI technology. An official from a domestic AI company said, “Concerns are growing that the status of Korea and Japan may be reversed due to the Japanese government’s policy efforts to prioritize domestic companies.”
The EU exempts domestic AI companies from regulation
European countries also follow a dual policy of protecting their own companies and regulating large technology companies like the United States. The European Union (EU) passed the AI law last month. The key is to introduce transparency rules to require data disclosure and risk assessment of AI systems deemed high risk. Breaching this can result in a fine of up to 7% of global sales depending on the type.
AI foundation models using open source models released to the outside world are exempt from regulation. The analysis is that it has taken into account that leading European AI companies, such as Mistral AI (France) and Aleph Alpha (Germany), may be at a disadvantage. Both Mistral AI and Aleph Alpha use an open source model.
The United States and China, competing for AI hegemony, are not much different. In October last year, China issued security guidelines for companies providing productive AI services. The key is that the data used to train AI models should not contain illegal or harmful information. This includes actions that overthrow the socialist system, damage the national image, and undermine national unity and social stability. The industry assessment is that it is almost impossible for foreign companies to launch productive AI services in China. The US is focusing its efforts on excluding Chinese companies. US President Joe Biden signed a bill on the 24th that states that if TikTok is not sold to non-Chinese capital within 360 days, it will be removed from the US App Store. The US Congress passed this bill, saying that problems such as invasion of privacy and security threats would arise if TikTok, owned by the Chinese company ByteDance, transferred the personal information of Americans to Chinese authorities.
Korea is the exact opposite of the global trend. There is a tendency to strengthen regulations on domestic platform companies that lead the AI industry. As the Fair Trade Commission pushes to enact the Fair Platform Competition Promotion Act which targets major domestic and foreign platform companies, the US government appears to be blocking the passage of the bill through the US Embassy in Korea and Chamber American trade in Korea. It is very likely that the AI bill, which contains basic details on the promotion and regulation of AI, will be repealed at the end of the term of the 21st National Assembly.
Reporter Seungwoo Lee leeswoo@hankyung.com
#Japan #openly #shows #favoritism #warns #heavy #fines